what is normal red blood cell count in urine How we report white blood cells count in urinalysis
A complete blood count (CBC) test is a common blood test that provides essential information about a person’s overall health. By analyzing different components of blood, a CBC can help identify various medical conditions and monitor the effectiveness of treatments.
Red Blood Cell Analysis
In a CBC, one of the key parameters evaluated is the red blood cell (RBC) count. RBCs are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and removing carbon dioxide. An optimal RBC count is necessary for maintaining proper oxygenation of organs and tissues.
 In normal control and pregnant women, a CBC can provide valuable insights into red blood cell parameters. This allows healthcare professionals to assess any abnormalities and provide appropriate medical interventions if needed. It is important to note that the reference ranges for RBC count may vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and altitude.
In normal control and pregnant women, a CBC can provide valuable insights into red blood cell parameters. This allows healthcare professionals to assess any abnormalities and provide appropriate medical interventions if needed. It is important to note that the reference ranges for RBC count may vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and altitude.
Causes of High Red Blood Cell Count
A high red blood cell count, known as erythrocytosis or polycythemia, can indicate various underlying medical conditions. Understanding the causes of high RBC count is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
 There are several factors that can contribute to an elevated RBC count. One common cause is chronic hypoxia, where the body doesn’t receive enough oxygen. This can occur in conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), congestive heart failure, or living at high altitudes.
There are several factors that can contribute to an elevated RBC count. One common cause is chronic hypoxia, where the body doesn’t receive enough oxygen. This can occur in conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), congestive heart failure, or living at high altitudes.
Another possible cause is polycythemia vera, a rare blood disorder characterized by the overproduction of red blood cells in the bone marrow. This condition is usually accompanied by other symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, and difficulty breathing.
Furthermore, conditions that lead to increased secretion of erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production, can also contribute to a high RBC count. These conditions include kidney tumors, renal cysts, and certain types of lung tumors.
It’s important to note that a high RBC count may not always indicate a serious medical condition. In some cases, it may be a transient response to factors such as dehydration, strenuous exercise, or smoking. However, if an elevated RBC count persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
A complete blood count with a focus on red blood cell analysis is a valuable tool for healthcare professionals in assessing overall health and identifying potential underlying medical conditions. By understanding the causes and implications of a high RBC count, healthcare providers can provide appropriate interventions and ensure the well-being of their patients.
If you are searching about RBC in Urine: Causes and Clinical Significations - Lab Tests Guide you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Pictures about RBC in Urine: Causes and Clinical Significations - Lab Tests Guide like Full Blood Count Interpretation : CBC (Complete Blood Count) Test in, How we report white blood cells count in urinalysis | Medical Laboratories and also Full Blood Count Interpretation : CBC (Complete Blood Count) Test in. Here it is:
RBC In Urine: Causes And Clinical Significations - Lab Tests Guide
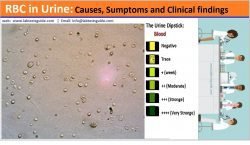 www.labtestsguide.comurine rbc hematuria
www.labtestsguide.comurine rbc hematuria
How We Report White Blood Cells Count In Urinalysis | Medical Laboratories
 www.medical-labs.neturinalysis
www.medical-labs.neturinalysis
Causes Of High Red Blood Cell Count - موقع معلومه صحيه
 www.medican-health.comcold agglutinin polycythemia anemia elevated rimedi hemolytic medican trattamenti bianchi globuli basso fatigue cellulite
www.medican-health.comcold agglutinin polycythemia anemia elevated rimedi hemolytic medican trattamenti bianchi globuli basso fatigue cellulite
What Do Normal Red Blood Cells Look Like? | Pathology Student
 www.pathologystudent.comnormal blood cells red look central pallor rbcs smear cell iron blood1 anemia rbc erythrocytes poikilocytosis human normochromic microscopic abnormal
www.pathologystudent.comnormal blood cells red look central pallor rbcs smear cell iron blood1 anemia rbc erythrocytes poikilocytosis human normochromic microscopic abnormal
Full Blood Count Interpretation : CBC (Complete Blood Count) Test In
 ruma-ewa.blogspot.comblood pregnancy differential interpretation values
ruma-ewa.blogspot.comblood pregnancy differential interpretation values
Normal blood cells red look central pallor rbcs smear cell iron blood1 anemia rbc erythrocytes poikilocytosis human normochromic microscopic abnormal. Full blood count interpretation : cbc (complete blood count) test in. How we report white blood cells count in urinalysis